using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ObserverPattern
{
public interface IObserver
{
void Update(float temp, float humidity, float pressure);
}
public interface ISubject
{
void RegisterObserver(IObserver o);
void RemoveObserver(IObserver o);
void NotifyObservers();
}
public interface IDisplayElement
{
void Display();
}
public class WeatherSubject : ISubject
{
readonly List<IObserver> observers;
float temperature;
float pressure;
float humidity;
public void GetterMeasurements(float inTemperature, float inHumidity, float inPressure)
{
temperature = inTemperature;
humidity = inHumidity;
pressure = inPressure;
NotifyObservers();
}
public WeatherSubject()
{
observers = new List<IObserver>();
}
#region ISubject Members
public void RegisterObserver(IObserver o)
{
observers.Add(o);
}
public void RemoveObserver(IObserver o)
{
observers.Remove(o);
}
public void NotifyObservers()
{
foreach ( IObserver observer in observers )
{
observer.Update(temperature, humidity, pressure);
}
}
#endregion
}
}'Design Patterns'에 해당되는 글 19건
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample - Observer Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample - Factory Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample : Facade Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample - Decorator Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample : Adapter Pattern 2
- 2009.01.07 Code Sample : Adapter Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Head First Design Patterns
- 2009.01.07 Structural Pattern
- 2009.01.07 Pattern Comparison
object의 생성부분을 처리하는 class를 factory로 한다.
특정한 객체를 만들어서 넘겨줄때, 또는 객체를 생성하고, 준비하는 과정에 대한 기본적인 내용이 필요한 경우에 Factory를 만들어서 Factory에서 처리하도록 한다.
using System;
namespace FactoryPattern1
{
public interface IPizzaStore
{
Pizza OrderPizza(string pizzaName);
}
public interface IPizzaFactory
{
Pizza CreatePizza(string pizzaName);
}
public class MyHomePizzaFactory : IPizzaFactory
{
#region IPizzaFactory Members
public Pizza CreatePizza(string pizzaName)
{
return new Pizza() { Name = pizzaName + " Sweet MyHome" };
}
#endregion
}
public class MyHomePizzaStore : PizzaStore, IPizzaStore
{
IPizzaFactory pizzaFactory;
public MyHomePizzaStore(IPizzaFactory pizzaFactory)
{
this.pizzaFactory = pizzaFactory;
}
#region IPizzaStore Members
public Pizza OrderPizza(string pizzaName)
{
Pizza pizza = pizzaFactory.CreatePizza(pizzaName);
PreparePizza(pizza);
CutPizza(pizza);
//this method is changable : in my home, we eat pizza with no boxing.
return pizza;
}
#endregion
}
public class HostwayPizzaFactory : IPizzaFactory
{
#region IPizzaFactory Members
public Pizza CreatePizza(string pizzaName)
{
return new Pizza() { Name = pizzaName + " HostwayPizza" };
}
#endregion
}
public class HostwayPizzaStore : PizzaStore, IPizzaStore
{
IPizzaFactory pizzaFactory;
public HostwayPizzaStore(IPizzaFactory pizzaFactory)
{
this.pizzaFactory = pizzaFactory;
}
#region IPizzaStore Members
public Pizza OrderPizza(string pizzaName)
{
Pizza pizza = pizzaFactory.CreatePizza(pizzaName);
PreparePizza(pizza);
CutPizza(pizza);
BoxingPizza(pizza);
return pizza;
}
#endregion
}
public abstract class PizzaStore
{
public string CutPizza(Pizza pizza)
{
return "Cutting Pizza";
}
public string PreparePizza(Pizza pizza)
{
return "Prepare Pizza";
}
public string BoxingPizza(Pizza pizza)
{
return "Boxing pizza";
}
}
public class Pizza
{
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
복잡한 여러개의 Interface를 단순화하기 위한 Pattern.
하나이상의 Class의 복잡한 interface를 단순한 Facade로 덮어주는 Pattern.
용도에 따른 변경에 주안점을 주게 된다 : 하나의 복잡한 일을 하는 것에 대한 쉬운 접근 방법의 제공
단순화된 인터페이스를 제공하면서도, 클라이언트에서 필요로 한다면 sub class의 모든 기능을 제공할 수 있어야지 된다.
public interface IHomeTheaterFacade
{
void TurnOnMovie();
void TurnOffMovie();
}
public class HomeTheaterFacade : IHomeTheaterFacade
{
object amp;
object tuner;
object dvdPlayer;
object dvd;
object projector;
object screen;
public HomeTheaterFacade(object amp, object tuner, object dvdPlayer, object dvd, object projector, object screen)
{
this.amp = amp;
this.tuner = tuner;
this.dvdPlayer = dvdPlayer;
this.dvd = dvd;
this.projector = projector;
this.screen = screen;
}
#region IHomeTheaterFacade Members
public void TurnOnMovie()
{
//Note : Do some thing
}
public void TurnOffMovie()
{
//Note : Do some thing
}
#endregion
}
Decorator pattern에서는 객체에 추가적인 요소를 동적으로 첨가하는 것이 목적이다.
하나의 class에서 다른 class로 확장되어서 나가는 하나의 그림에서 다른 그림으로 확장되어 나가는 방법을 제시할 수 있으면 된다.
Decorator Pattern의 주안점은 생성자이다. 생성자에서 자신이 상속받은 interface를 인자로 받아서, 전의 객체에 장식(decorator)를 해주는 것이 최선의 방법이 된다.
using System;
namespace DecoratorPattern
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
Photo photo1 = new Photo(); //With Frame photo
Photo photo2 = new Photo(); //With Stamp & Frame Photo
PhotoFrame photoFrame = new PhotoFrame(photo1);
PhotoFrame photoFrame2 = new PhotoFrame(photo2);
PhotoStamp photoStamp = new PhotoStamp(photoFrame2);
Console.WriteLine(photoFrame.Display());
Console.WriteLine(photoStamp.Display());
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public interface IPhoto
{
string Display();
string Print();
}
public class Photo : IPhoto
{
#region IPhoto Members
public string Display()
{
return "Display Photo";
}
public string Print()
{
return "Print Photo";
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// Photo with a Frame.
/// </summary>
public class PhotoFrame : IPhoto
{
readonly IPhoto originalPhoto;
public PhotoFrame(IPhoto originalPhoto)
{
this.originalPhoto = originalPhoto;
}
#region IPhoto Members
public string Display()
{
return originalPhoto.Display() + " with Frame";
}
public string Print()
{
return originalPhoto.Print() + " with Frame";
}
#endregion
}
public class PhotoStamp : IPhoto
{
readonly IPhoto photo;
public PhotoStamp(IPhoto photo)
{
this.photo = photo;
}
#region IPhoto Members
public string Display()
{
return photo.Display() + " with Stamp.";
}
public string Print()
{
return photo.Print() + " with Stamp";
}
#endregion
}
}
하나의 옛날 Interface에서 새로운 Interface로의 전환이 이루어지고, 지원되지 않는 interface가 존재하게 될때에.
public interface IEnumerationExam
{
bool HasMoreElements();
void NextElement();
}
public interface IIterator
{
bool HasNext();
void Next();
void Remove();
}
public class EnemurationIterator : IIterator
{
private IEnumerationExam iEnumerationExam;
#region IIterator Members
public bool HasNext()
{
return iEnumerationExam.HasMoreElements();
}
public void Next()
{
iEnumerationExam.NextElement();
}
public void Remove()
{
throw new NotSupportedException();
}
#endregion
}
IOldBookStoreSystem을 구현한 OldBookStore을 아래와 같이 구현되어 있는 NewBookStore에서 사용하고자 할때.
같은 또는 비슷한 기능들이 각기 다른 interface로 구현되어 있을때 사용하는 pattern이 된다.
public class NewBookStore
{
public INewBookStoreSystem bookStoreSystem;
}
public interface INewBookStoreSystem
{
void BuyBook(string isbnNumber, string cardNumber);
void ChangeBook(string cardNumber);
}
//OldBookStore
public interface IOldBookStoreSystem
{
void BuyBook(string bookTitle, int costMoney);
void ChangeBook(string bookTitle, DateTime buyDate);
void CloseStore();
}
public class OldBookStore : IOldBookStoreSystem
{
public void BuyBook(string bookTitle, int costMoney)
{
Console.WriteLine("Buy book Title");
}
public void ChangeBook(string bookTitle, DateTime buyDate)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("Change Book : {0}", buyDate));
}
public void CloseStore()
{
Console.WriteLine("Close the store.");
}
}
이때에 새로운 INewBookStoreSystem을 이용. (INewBookStoreSystem이 adapter interface가 된다.)
public class OldBookStoreAdapter : INewBookStoreSystem
{
OldBookStore oldBookStore = new OldBookStore();
#region INewBookStoreSystem Members
public void BuyBook(string isbnNumber, string cardNumber)
{
//NOTE : Find book title using isbn number
string bookTitle = string.Empty;
//NOTE : send bill
int price = 1000;
oldBookStore.BuyBook(bookTitle, price);
}
public void ChangeBook(string cardNumber)
{
//NOTE : Find card list using cardNumber
//NOTE : Find bookTItle and buyDate
DateTime buyDate = DateTime.Now;
string bookTitle = string.Empty;
oldBookStore.ChangeBook(bookTitle, buyDate);
}
#endregion
}
스토리가 있는 패턴 학습법

Design pattern에 대한 책은 찾아보면서 여러가지로 생각도 많이 들고, 보고 나서도 어떻게 사용해야지 될지 모르겠다는 생각이 무척 많이 든다. C# 3.0 Design pattern은 다 보고 나서, 과연 어디에 사용할 수 있을지 모르겠다는 생각만 무척 많이 들고, 상속을 이용한 구성만이 계속 머리에 남고 있을때 보기 시작한 책.
이번에는 책 한권 제대로 정리좀 해봐야지 될텐데. --;
1. 바뀌는 부분은 캡슐화 된다.
2. 상속보다는 구성을 이용한다. (!! 가장 중요한 일이며, 가장 안지켜지는 일. -_-)
3. 구현이 아닌 interface에 맞춰서 프로그래밍한다.
4. 서로 상호작용을 하는 객체 사이에서는 가능하면 느슨하게 결합하는 디자인을 사용해야지 된다.
5. Class는 확장에 대해서는 열려있어야지만 변경에 대해서는 닫혀있어야지 된다.
6. 추상화된 것에 의존하라. 구상 class에 의존하지 않아야지 된다. (2번 항목과 같이 연결되는 부분. 이 부분에 대한 내용을 좀더 고민할 필요가 있음.)
Design Pattern에 대해서 공부를 할때마다 느끼는 가장 큰 하나.
: 공부할때, 내가 이런 방법이 코딩에 좋겠다.. 싶어서 예전에 썼던 것들이 다 패턴이였구나.. 하는 생각이 들때가 많다. --;
SYNCmailMobile이 CommandPattern을 만들어서 구성된 것을 이제야 깨닫게 되었다니.. -_-;;
Structual Pattern은 system이 design이 될때, 또는 유지보수 또는 확장시에 고려되게 된다.
특히 구버젼 시스템에 대한 확장시에 특히 유용하게 된다. 새로운 요구사항이 들어왔을 때에, 기존의 Class를 변경하는 것이 아닌, Decorator pattern을 이용해서 기존의 class를 유지하는 형태로 구현되게 된다.
- 존재하는 객체에 대해서 빈번하게 새로운 작업이 행해지게 될때,(decorator)
- 객체에 대한 동작을 행할때, (proxy)
- 요구시에 비용이 많이 드는 객체를 생성할때, (proxy)
- interface의 개발과 process에 의존적인 component를 구현할때, (bridge)
- 서로 양립되지 않는 interface를 서로간에 일치시킬 때 (adapter)
- 작고 많은 객체들의 비용을 줄일때 (flyweight)
- 하나의 entry point를 갖는 여러개의 subsystem을 새롭게 개편시킬 때 (Facade)
- 실행시에 객체를 선택 또는 변경시킬때 (Bridge)
- 복잡한 subsystem을 간략화 시킬때 (Facade)
- single objects와 composite object를 하나의 방법으로 다룰때(Composite)
Decorator Pattern
Illustration
Decorator pattern은 존재하는 object에 새롭게 더하는 것이 된다.
원 객체는 decorations에 대해서 알지 못하고, 그것에 대하여 관여하지 않는다.
모든 객체는 모든 option을 가지지 않고, 큰 일을 하나가 도맡아서 하지 않는다.
모든 decorations는 서로간에 연관되게 된다.
docorations는 서로간에 결합될 수 있고, mix-and-match가 되게 된다.
example
1. 하나의 그림이 있고, 그 그림에 tag를 달 수가 있다. tag를 하나 이상을 달 수 있으며, 그 tag는 각기 다른 tag를 다는 것이 가능하다.
using System;
namespace PhotoDecorator
{
public interface IPhoto
{
void Draw();
}
public class Photo : IPhoto
{
public void Draw()
{
Console.WriteLine("Draw Original Photo!!");
}
}
public class Tag1 : IPhoto
{
IPhoto component;
public Tag1(IPhoto component)
{
this.component = component;
}
public void Draw()
{
component.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Draw tag1 into photo");
}
}
public class Tag2 : IPhoto
{
IPhoto component;
public Tag2(IPhoto component)
{
this.component = component;
}
public void Draw()
{
component.Draw();
Console.WriteLine("Draw tag2 into photo");
}
}
public class Client
{
public static void DrawPicture(string pictureName, IPhoto photo)
{
Console.WriteLine( string.Format("Picture : {0}", pictureName));
photo.Draw();
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Photo originalPhoto1 = new Photo();
Photo originalPhoto2 = new Photo();
Tag1 tag1WithPhoto = new Tag1(originalPhoto1);
Tag2 tag2WithPhoto = new Tag2(originalPhoto2);
Client.DrawPicture("Original Photo with Tag1", tag1WithPhoto);
Client.DrawPicture("Original Photo with Tag2", tag2WithPhoto);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}2. windows를 하나 설치 한 후에, MS SQL과 Visual Studio를 설치시켜줘야지되는 그러한 환경에 대한 구현을 생각해보자.
using System;
namespace InstallWindows
{
public interface IInstall
{
void Install();
}
public class WindowsInstaller : IInstall
{
#region IInstall Members
public void Install()
{
Console.WriteLine("Windows Install complete");
}
#endregion
}
public class MsSqlInstaller : IInstall
{
IInstall windowsComponent;
public MsSqlInstaller(IInstall component)
{
windowsComponent = component;
}
#region IInstall Members
public void Install()
{
windowsComponent.Install();
Console.WriteLine("MSSQL install complete!!");
}
#endregion
}
public class MsVisualStudioInstaller : IInstall
{
IInstall windowsComponent;
public MsVisualStudioInstaller(IInstall component)
{
windowsComponent = component;
}
#region IInstall Members
public void Install()
{
windowsComponent.Install();
Console.WriteLine("MS Visual Studio Install complete!!");
}
#endregion
}
public class Client
{
public static void InstallWIndows(string target, IInstall component)
{
Console.WriteLine("====={0}=====", target);
component.Install();
}
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
WindowsInstaller windows1 = new WindowsInstaller(); //windows와 ms sql을 설치
WindowsInstaller windows2 = new WindowsInstaller(); //windows와 ms visual studio를 설치
WindowsInstaller windows3 = new WindowsInstaller(); //windows와 ms sql, ms visual studio를 설치
MsSqlInstaller sqlInstaller = new MsSqlInstaller(windows1);
Client.InstallWIndows("Windows with ms sql", sqlInstaller);
MsVisualStudioInstaller vsInstaller = new MsVisualStudioInstaller(windows2);
Client.InstallWIndows("Windows with visual studio", vsInstaller);
MsVisualStudioInstaller vsAndSqlInstaller = new MsVisualStudioInstaller(new MsSqlInstaller(windows3));
Client.InstallWIndows("Windows with ms sql and visual studio", vsAndSqlInstaller);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Use
- 하나의 기본적 동작이 있고, 그 동작에 대한 추가 동작에 대하여 만드는 것이 가능하다. (위의 예제와 같이, 윈도우를 하나 설치하고, 그 다음에 다른 동작을 행할 때, 그 윈도우에 대하여 동작을 넣는 것이 가능하다.)
- C#의 I/O API가 Decorator pattern으로 되어 있다. System.IO.Stream에서 다른 Stream들은 IStream을 생성자로 받아서 동작을 행하도록 되어있다.
- Windows control의 경우에, System.Windows.Control을 상속받는 class들은 모두 Decorator pattern으로 만들어져 있다. ListBox를 그린 후에 Border를 진하게 만들어 준다던가 하는 식의 동작들은 모두 Decorator pattern으로 구성되게 된다.
Proxy Pattern
Role
객체에 대한 생성 및 접근을 제한을 줄 필요가 있을때 주로 사용된다. 이때 Proxy의 경우에는 작은 public method로 열린 객체로서 만들어지고, proxy로 보호되는 객체는 private로 닫힌 객체로서 생성 및 접근에 제한을 주게 된다.
Example
1. Logon이 되지 않은 상태와 Logon이 된 상태에서의 View와 객체의 Request 의 제한을 주는 경우
using System;
namespace ProxyPattern
{
public interface ISubject
{
void DoSomeThing();
}
internal class Subject
{
public void DoSomeThing()
{
Console.WriteLine("Do SomeThing in wanted object");
}
}
public class ProtectionSubject : ISubject
{
private Subject subject; //Proxy에 의해서 접근 및 생성이 제한 받는 Class
public bool Authenticate(string password)
{
if ( password.ToLower() == "password" )
{
subject = new Subject();
return true;
}
else
{
subject = null;
return false;
}
}
#region ISubject Members
public void DoSomeThing()
{
if ( subject != null )
{
subject.DoSomeThing();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Authenticate First!!");
}
}
#endregion
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
ProtectionSubject protectionSubject = new ProtectionSubject();
protectionSubject.DoSomeThing();
protectionSubject.Authenticate("윤영권");
protectionSubject.DoSomeThing();
protectionSubject.Authenticate("password");
protectionSubject.DoSomeThing();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
2. Install이 되지 않은 상태에서 Computer를 접근하는 경우 (proxy와 decorator를 둘다 적용한 경우)
using System;
namespace ProxyAndDecorator
{
public interface IWindowProxy
{
void DoSomeThing();
}
public interface IInstall
{
void Install();
}
public class WindowsProxy : IWindowProxy
{
IInstall installObject;
public void CreateObject(string type)
{
if ( type == "none" )
{
installObject = new WindowsInstaller();
}
else if ( type == "mssql" )
{
WindowsInstaller windowsInstaller = new WindowsInstaller();
installObject = new MsSqlInstaller(windowsInstaller);
}
else if ( type == "vs" )
{
WindowsInstaller windowsInstaller = new WindowsInstaller();
installObject = new MsVisualStudioInstaller(windowsInstaller);
}
}
#region IWindowProxy Members
public void DoSomeThing()
{
if ( installObject != null )
{
IWindowProxy w = ( IWindowProxy )installObject;
w.DoSomeThing();
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("First CreateObject");
}
}
#endregion
}
public class WindowsInstaller : IInstall, IWindowProxy
{
internal WindowsInstaller()
{
}
#region IInstall Members
public void DoSomeThing()
{
Console.WriteLine("Do Something in original windows");
}
public void Install()
{
Console.WriteLine("Windows Install complete");
}
#endregion
}
public class MsSqlInstaller : IInstall, IWindowProxy
{
IInstall windowsComponent;
internal MsSqlInstaller(IInstall component)
{
windowsComponent = component;
}
#region IInstall Members
public void Install()
{
windowsComponent.Install();
Console.WriteLine("MSSQL install complete!!");
}
#endregion
#region IWindowProxy Members
public void DoSomeThing()
{
Console.WriteLine("Do Something in ms sql");
}
#endregion
}
public class MsVisualStudioInstaller : IInstall, IWindowProxy
{
IInstall windowsComponent;
internal MsVisualStudioInstaller(IInstall component)
{
windowsComponent = component;
}
#region IInstall Members
public void Install()
{
windowsComponent.Install();
Console.WriteLine("MS Visual Studio Install complete!!");
}
#endregion
#region IWindowProxy Members
public void DoSomeThing()
{
Console.WriteLine("Do SomeThing in Visual Studio");
}
#endregion
}
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
WindowsProxy proxy = new WindowsProxy();
proxy.DoSomeThing();
proxy.CreateObject("none");
proxy.DoSomeThing();
proxy.CreateObject("mssql");
proxy.DoSomeThing();
proxy.CreateObject("vs");
proxy.DoSomeThing();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Bridge Pattern
Role
Bridge Pattern은 구현과 추상화의 결합도를 낮추는데 목표가 있다. Bridge pattern은 기존에 존재하고 계속 남아있어야지 되는 구버젼에서 새로운 신버젼이 있을때에 유용한 패턴이다 .이미 구현된 추상화에 맞추어진 client code는 변경되지 않지만 client code는 자신이 원하는 어떤 버젼에서 동작될지를 결정해줘야지 된다.
Illustration
여러개의 .NET Framework가 있는 상황에서, S/W가 어떠한 .NET Framework를 골라서 사용해야지 될지를 고민하는 상황과 비슷하게 만들어진다.
Design
상속은 각기 다른 추상화의 구현에 대하여 일반적인 방법이다. 그렇지만, 구현은 추상화의 영역에 제한이 되게 되며, 추상화의 의존적인 상태에서의 변경은 제한적이 된다. Bridge pattern은 하나 이상의 추상화에 대한 상속을 통해 이미 구버젼의 추상화가 되어 있는 상황에서 추상화에 상속을 하는 것이다. 같은 추상화에서의 각각의 상속을 통해 추상화의 범위를 넓히는 것이 가능하다.
구현에 대한 동작을 Bridge에 위임하고, 동작에 대한 것을 따로 나누어주는 것으로서 구현하게 되는데, Bridge를 개선하는 것으로 전체 Class의 변경 없이 구현이 가능해진다.
using System;
namespace BridgePattern
{
public interface IBridge
{
void Add(string message);
void Add(string friend, string message);
void Poke(string who);
}
/// <summary>
/// Bridge에 의하여 구현되어진 Class
/// 구현에 의한 추상화만을 가지고 있고, 실질적인 동작은 Bridge에서 이루어지게 된다.
/// 같은 추상화에서 다른 동작을 행할때, Bridge를 변경시켜서 가능해진다.
/// </summary>
class Portal
{
readonly IBridge bridge;
public Portal(IBridge bridge)
{
this.bridge = bridge;
}
public void Add(string message)
{
bridge.Add(message);
}
public void Add(string friend, string message)
{
bridge.Add(friend, message);
}
public void Poke(string who)
{
bridge.Poke(who);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Proxy에 의해서 보호받는 Class
/// </summary>
class Subject
{
public string SubjectName { get; set; }
public void DisplayName()
{
Console.WriteLine(SubjectName);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Proxy
/// </summary>
class MySubject
{
private Subject subject;
public void Authritize(string password)
{
subject = new Subject();
}
public void DisplayName()
{
if ( subject == null )
{
Console.WriteLine("Subject is null");
}
else
{
subject.DisplayName();
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Bridge Pattern으로 만들어진 Class
/// 실질적인 동작이 이루어지는 Class
/// </summary>
public class MyBook : IBridge
{
public string Name { get; set; }
private MySubject mySubject;
private static int users;
public MyBook(string name, string password)
{
mySubject = new MySubject();
Name = name;
users++;
mySubject.Authritize(password);
}
#region IBridge Members
public void Add(string message)
{
mySubject.DisplayName();
Console.WriteLine(message);
}
public void Add(string friend, string message)
{
mySubject.DisplayName();
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} : {1}", friend, message));
}
public void Poke(string who)
{
mySubject.DisplayName();
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}", who));
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// C# 3.0 Extension : Class Extension, Bridge pattern에서 Bridge의 확장에 유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
/// </summary>
static class OpenBookExtensions
{
public static void SuperPoke(this Portal me, string who, string message)
{
me.Add(who, message);
}
}
class BridgePattern
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Portal me = new Portal(new MyBook("Judith", "password"));
me.Add("Hello world");
me.Add("Today I worked 18 hours");
Portal tom = new Portal(new MyBook("Tom", "password2"));
tom.Poke("Judith-1");
tom.SuperPoke("Judith-1", "hugged");
tom.Add("Judith-1", "Poor you");
tom.Add("Hey, I'm on OpenBook - it's cool!");
}
}
}
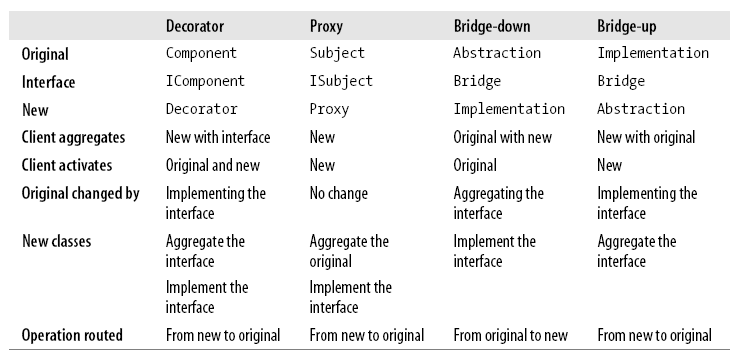
Summary :
Decorator pattern
하나의 동작(interface)에서 각기 다른 동작이지만, 서로간에 영향을 줄 수 있는 상황에서 사용한다. 객체의 생성자에 다른 같은 interface를 갖는 객체를 받아서, 하나의 interface에서 같은 동작을 행하도록 만들어준다. 이러한 방법은 각각의 객체에 자신이 하는 일을 구현하게 되며, 마지막으로 decorate 된 객체에서 모든 객체에 대한 동작을 일괄적으로 처리할 수 있도록 해준다. 또 다른 추가적인 동작이 필요할 때, 다른 decorator를 만들어서, 그 decorator를 사용하면 모든 객체에 대한 동작을 일괄적으로 만들어 줄 수 있다.




